
Be sure to visit our storage homepage for more information.
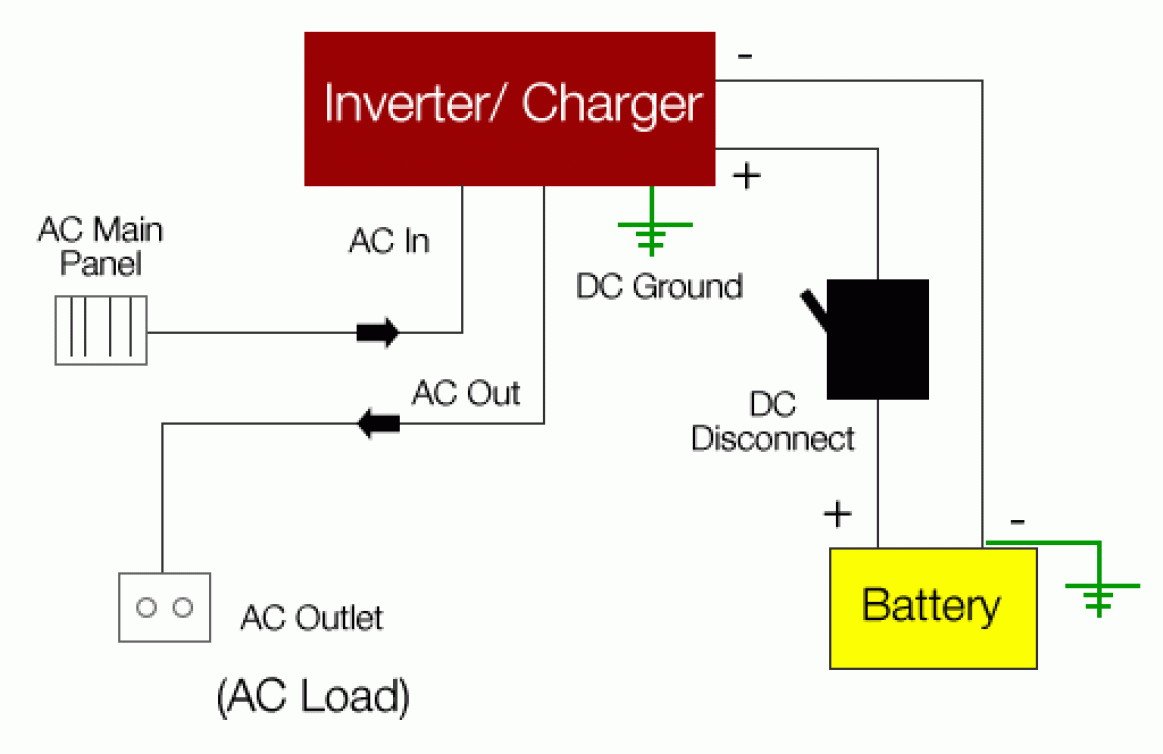
Inverters/Chargers are reliable power sources for continuous backup applications.
Usually, an inverter/charger has two modes:
1) Inverter Mode: This mode is the common off-grid inverter application in which the DC power from the batteries are converted into AC for powering home appliances. This is the most common application for off-grid battery backup systems.
During a blackout in the utility grid or in stationary applications or while driving in mobile applications, inverters/chargers automatically switch from utility power to battery backup power.
2) Standby or Charger Mode: The inverter/charger operates as a battery charger to convert incoming AC power into DC power in order to charge the battery. At the same time, most inverter/chargers currently on the market pass the incoming AC power directly to inverter/ charger's AC outputs to power the AC loads.
In which applications to use inverter/ chargers?
Inverters/Chargers are designed for EMS, RVs and other applications where reliable battery backup is necessary while on the road. The main advantage of an inverter/charger unit is the flexibility to charge the battery bank through a grid system. Although the units are mainly aimed to power off-grid systems that are powered by solar power, the inverter/ charger owner must know that they have the freedom to connect to grid anytime.
There are large sizes of inverter/chargers in the market that can fulfill the needs of a grid-tied cabin (home solar) system with a back-up battery bank.